Relationship Types
Bizagi offers four types of relationships between entities, providing greater flexibility in your data model.
Related Attribute Relationship
This is the most common relationship, where one instance of an entity is associated with one instance of another entity.
What distinguishes this relationship is the order in which it is created; mainly because it creates an attribute in one entity in reference to another but NOT both ways.
It is commonly used for relationships between a master entity and a parameter entity for drop-down lists (or combos) and between master entities.
These types of relationships are automatically created through the Data Model Wizard, when choosing the Entity type attribute.
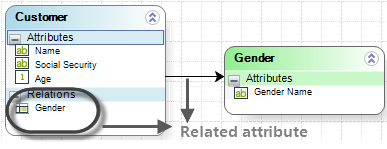
For example, a Customer has one gender, thus there is a Related Attribute between Customer and Gender entities. However, a gender will be assigned to many customers.
The Related Attribute relationship creates an attribute in the Customer entity, shown under Relations, to reference the Gender (not both ways). You cannot reference a particular Customer from a Gender.
The relationship is modeled as a single arrow line.
One-to-One Relationship
One-to-one relationships are established when there is a single correspondence between two entities.
That is, each record from entity A is associated with a single record from entity B, and vice versa.
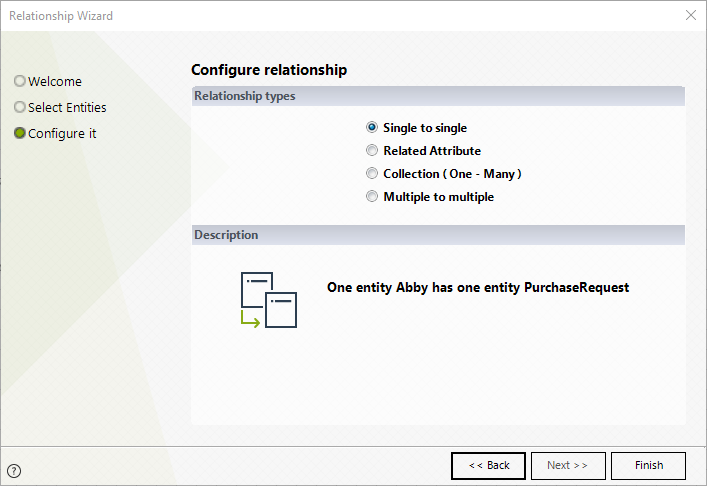
For example, imagine there are two entities, Employee and Computer.
There is a single-to-single relationship between the two entities because each employee is associated with just one computer, and one computer has been assigned to only one employee.
When this type of relationship is created, Bizagi will automatically create the attributes (foreign key) that relate the entities to each other.
The one-to-one relationship creates a foreign key attribute in each entity, shown under the respective Relations nodes, to reference the other entity (both ways).
The relationship is modeled as a double arrow line.

To Create a One-to-One Relationship:
-
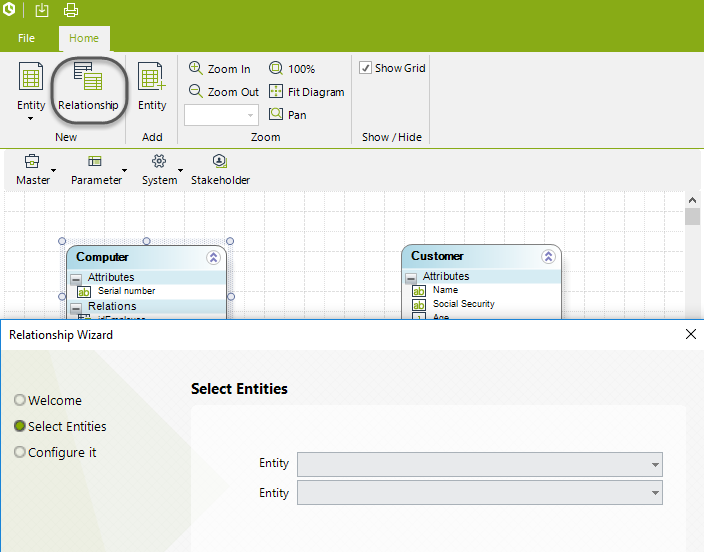
Open the second step of the Process Wizard: Model Data.
-
Click the Relationship button in the Home tab and select the two entities to be related.
-
Select the relationship type and click Finish.
Collection or One-to-Many Relationship
One-to-many relationships are established when one instance of an entity (entity A) can be associated with zero, one, or many instances of another entity (entity B).
However, for one instance of entity B, there is only one instance of entity A.
In Bizagi, this relationship is called a Collection.
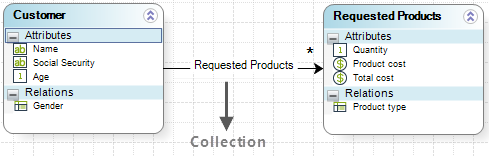
For example, imagine there are two entities: Customer and Requested Products.
The Customer (entity A) can have many Requested Products (entity B), but those products that were requested can only belong to one customer.
These types of relationships are automatically created through the Data Model Wizard, when selecting the Collection type attribute.
A collection is modeled as a single arrow line with an asterisk (*).
Note that no attributes are created and shown under Relations of the Customer entity for this relationship.
note_pin
Bear in mind that when deleting a one-to-many relationship, the foreign attribute is not deleted automatically.
Due to data integrity measures, the foreign attribute created must be deleted manually.
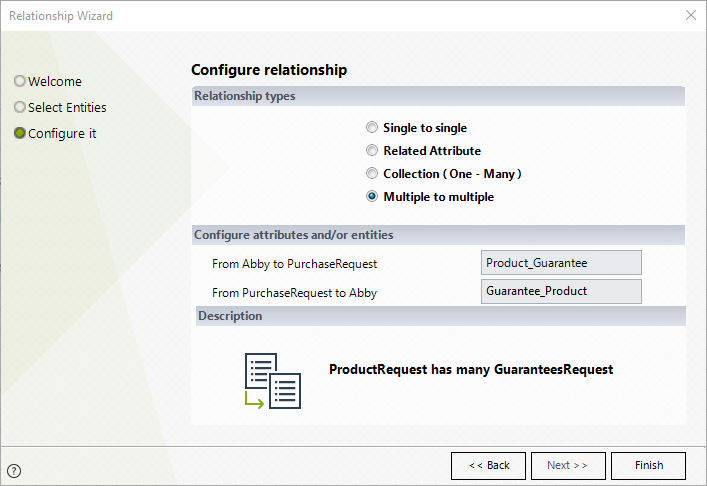
Multiple-to-Multiple Relationship
Multiple-to-multiple relationships are established when one instance of an entity (entity A) is associated with one, zero, or many instances of another entity (entity B), and one instance of entity B is associated with one, zero, or many instances of entity A.
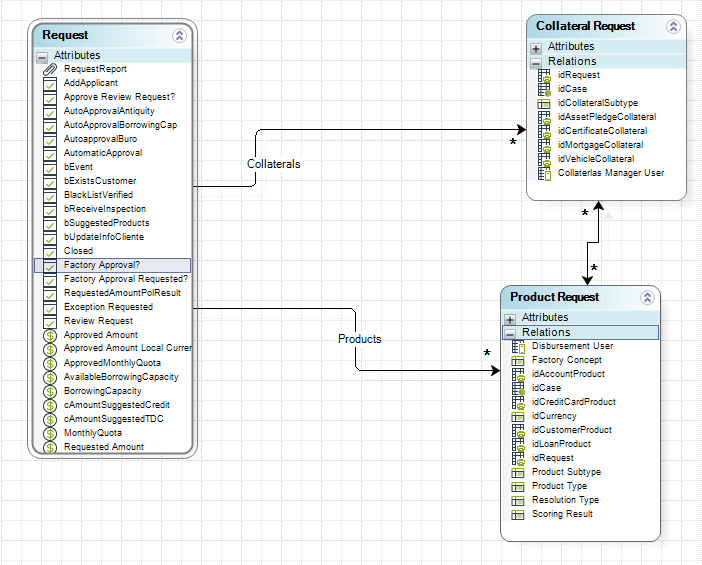
For example, in a Loan Request Process, a request may have several products (personal loan, credit card) and several collaterals or guarantees to cover the products (co-borrower, mortgage).
Each product may have many associated guarantees.
Thus, there is a multiple-to-multiple relationship between GuaranteesRequest and ProductsRequest:
A product can be covered by several guarantees of the request, and a guarantee can cover several products of the request.
A many-to-many relationship is modeled as a double arrow line with an asterisk (*) at each arrow end.
To Create a Multiple-to-Multiple Relationship:
-
Open the second step of the Process Wizard: Model Data.
-
Click the Relationship button in the Home tab and select the two entities to be related.
Then click Next.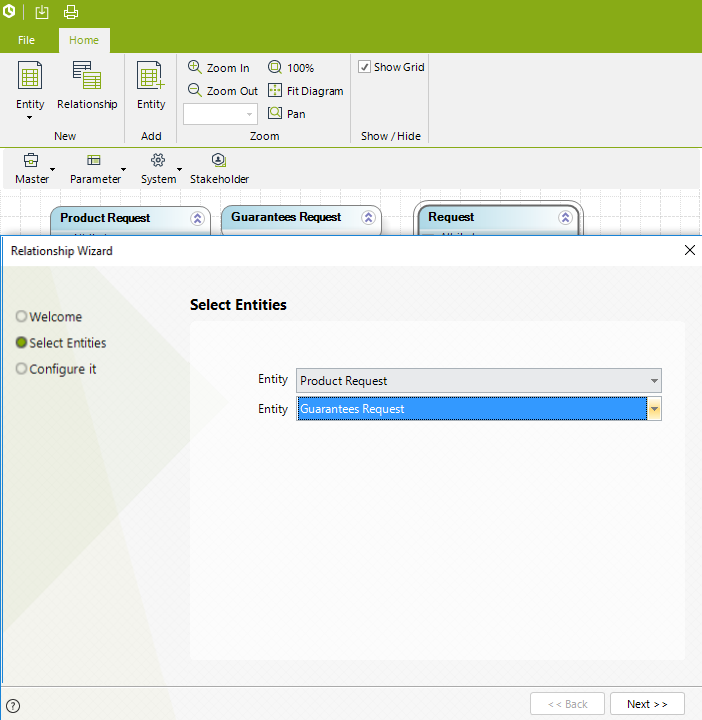
-
Select the relationship type.
Then type the names for both sides of the bidirectional relationship.- In the example, the relationship between the request products and its guarantees will be Product_Guarantee.
- The relationship between the guarantees and their covered products will be Guarantee_Products.
Then click Finish.